Coal/Gas/Electricity
A Game-Changer for the Coal Industry
Coal-fired power plants remain one of the largest sources of global electricity production, supplying more than 35% of the world’s energy needs. However, coal plants are also the biggest contributors to CO₂ emissions, accounting for 40% of global CO₂ emissions.
While renewables are growing, coal remains critical to energy security in major economies such as China, India, the United States, and Europe. The key challenge is reducing coal’s environmental impact without disrupting global energy supply.
A Viable Solution: Clean Coal Technology
The Thunderstorm Generator (TSG) Emission Technology is a breakthrough solution that:
- Retrofits existing coal plants—no need for costly new infrastructure.
- Achieves near-zero emissions, drastically cutting CO₂, CO, and SO₂.
- Maintains energy reliability without requiring nuclear investment.
- Supports a just energy transition, protecting jobs while meeting climate targets.
NOTE: The same dynamics below can be applied to Natural Gas Electricity generation
The Technology: The Thunderstorm Generator (TSG)
The TSG system is an advanced emission-control retrofit that applies plasmoid physics to transform pollutants into clean byproducts.
How It Works:
- Step 1: The system captures exhaust gases from coal combustion.
- Step 2: Using plasmoid technology, it breaks down harmful emissions at a molecular level.
- Step 3: Converts CO₂ into oxygen (O₂) and harmless compounds.
- Step 4: Reduces overall energy consumption, improving efficiency.
Tested and Validated Emission Reductions
- CO₂ Reduction: 99.56%
- CO Reduction: 98%
- SO₂ Reduction: 84.8%
The industry-certified results prove that coal plants can continue to operate while meeting strict emission regulations.
Impact on global emissions
Applying TSG technology to coal plants worldwide would result in unprecedented emission reductions, far surpassing current global climate goals.
1. CO₂ Reduction (99.56%)
- Massive impact on global carbon output—coal plants emit over 14.6 billion tons of CO₂ annually.
- Potential reduction of 14.5 billion tons, equivalent to eliminating emissions from over 3 billion cars.
2. CO Reduction (98%)
- Prevents carbon monoxide poisoning and air pollution-related deaths.
- Reduces urban smog, improving health and air quality in industrial regions.
3. SO₂ Reduction (84.8%)
- Cuts acid rain formation, protecting water and soil ecosystems.
- Reduces respiratory disease risks, especially in high-pollution areas.
With TSG, coal power can meet net-zero goals while remaining a viable energy source.
Coal Power’s Global Impact
1. Global Coal Power Emissions
- Coal generates 35% of global electricity but contributes 40% of energy-related CO₂ emissions.
- Total CO₂ emissions from coal power (2023): 14.6 billion tons.
- Main coal power users: China (4.6B tons), India (2.6B tons), USA (1.1B tons), EU (0.9B tons).
2. Applying TSG Technology Globally
By applying 99.56% CO₂ reduction to global coal plants:
- Total Coal Emissions Before TSG: 14.6 billion tons CO₂.
- Emissions After TSG: 58.4 million tons CO₂ (nearly eliminated).
- Total Reduction: 14.54 billion tons CO₂ annually!
3. Achieving Global Climate Goals
- The Paris Agreement calls for a 50% reduction in emissions by 2030.
- Applying TSG to global coal power plants alone would surpass that goal by 2.5 times.
- This would make net-zero by 2030 a reality, without eliminating coal jobs or causing energy instability.
Economic and Industrial Benefits
1. Cost Comparison: TSG vs. Other Technologies
|
Technology |
Cost Per Ton CO₂ Reduction |
Energy Efficiency Impact |
|---|---|---|
|
TSG Technology |
$10–$20 per ton |
+19.45% efficiency |
|
CO₂ Scrubbers |
$50–$100 per ton |
-20% efficiency loss |
|
Nuclear Power |
$17,000 per kW |
Slow adoption (15+ years) |
2. Why TSG Is a Better Alternative to Nuclear
- Nuclear energy is expensive and slow to deploy—coal can be cleaned immediately with TSG.
- No radioactive waste or safety concerns associated with TSG.
- TSG is an affordable and scalable solution, making the existing energy grid more sustainable.
3. Energy Security & Job Preservation
- Supports millions of coal industry jobs, while reducing emissions.
- Ensures stable energy supply, especially in countries dependent on coal.
- Encourages investment in clean technology, driving economic growth.
Future of Clean Coal Power
The Thunderstorm Generator (TSG) Emission Technology is the key to transforming the global energy sector. Instead of shutting down coal plants, TSG allows them to operate cleanly, efficiently, and cost-effectively.
The reality:
- Eliminating coal without a scalable alternative is not feasible.
- With TSG, coal becomes an ultra-low-emission energy source.
- A fast, affordable, and industry-proven solution is already available.
Environmental and Societal Benefits
- Reduces air pollution—fewer hospitalizations and respiratory diseases.
- Stabilizes energy markets—avoids energy crises caused by premature coal shutdowns.
- Protects industrial economies—ensures job security while reducing emissions.
- Achieves climate goals without sacrificing growth.
A Global Shift in Clean Energy
The world does not need to choose between economic growth and climate action.
- The Thunderstorm Generator (TSG) enables coal power to become a near-zero-emission energy source.
- By implementing this technology, coal plants can operate cleaner, longer, and more efficiently.
- Net-zero energy production is now possible without sacrificing energy security.
The future of coal is not elimination—it’s transformation.
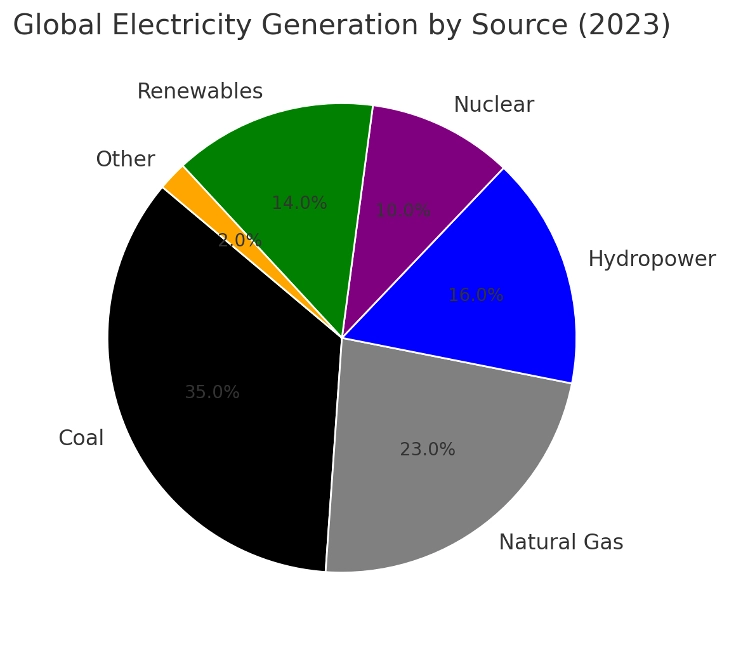
Global Electricity Generation by Source (2023)
Here is an infographic illustrating the global electricity generation mix (2023). It highlights coal’s dominant role, showing why cleaning coal power through TSG technology is crucial for achieving global climate goals.
Key Insights from the Chart
- Coal remains the largest single source of electricity (35%), making it a top priority for emission reduction.
- Natural gas (23%) and renewables (14%) play growing roles but are not yet capable of fully replacing coal.
- Nuclear (10%) is expensive and slow to expand, while hydropower (16%) is location-dependent.
Conclusion
- Coal isn’t going away soon—but it can be cleaned.
- TSG offers a near-zero-emission coal power solution to meet climate targets without energy shortages.
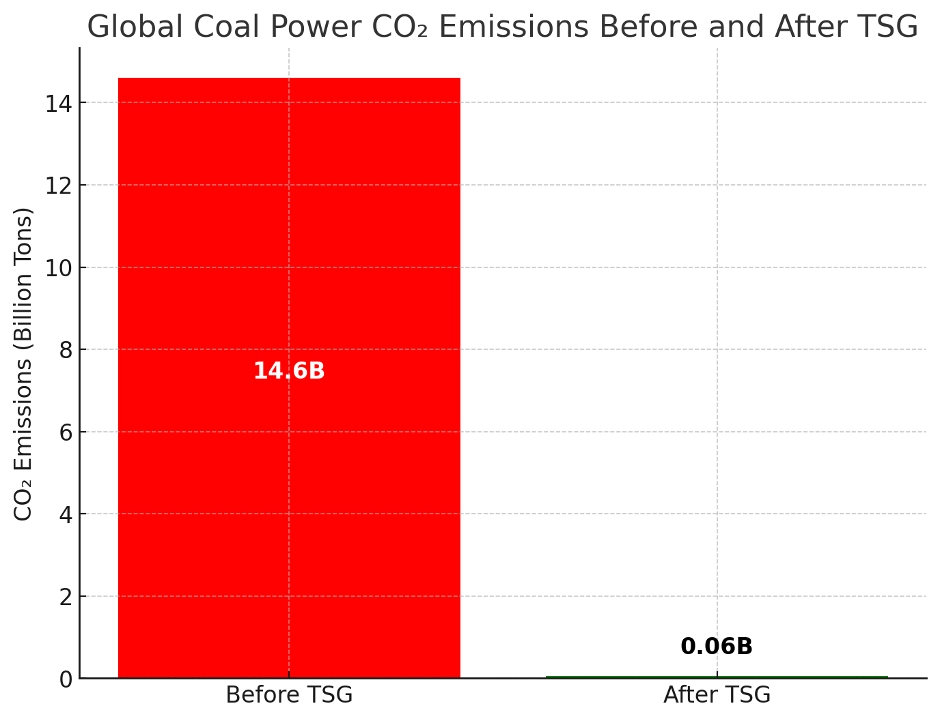
Global Power CO2 Emissions Before and After the TSG
Here is a bar chart illustrating global CO₂ emissions from coal power plants before and after TSG implementation.
Key Insights from the Chart
- Current global coal emissions: 14.6 billion tons CO₂ annually.
- Projected emissions after TSG implementation: Only 58.4 million tons CO₂ (99.56% reduction).
- Impact: Nearly eliminates CO₂ emissions from coal, making it a near-zero-emission energy source.
Conclusion
- SG transforms coal from the biggest CO₂ emitter into a clean energy solution.
- A global-scale rollout would massively accelerate net-zero climate goals.